how to convert biomass to energy
Biomass Energy - The Definitive Guide
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of biomass energy. From its sources and conversion processes to its environmental impact and potential benefits, we delve into everything you need to know about this renewable energy source.
1. What is biomass energy and how does it work?
Biomass energy refers to the energy derived from organic materials, such as plants, trees, agricultural crops, and even organic waste. It is harvested and processed through various conversion techniques to produce heat, electricity, or biofuels. The energy release is primarily achieved through biochemical and thermochemical processes.
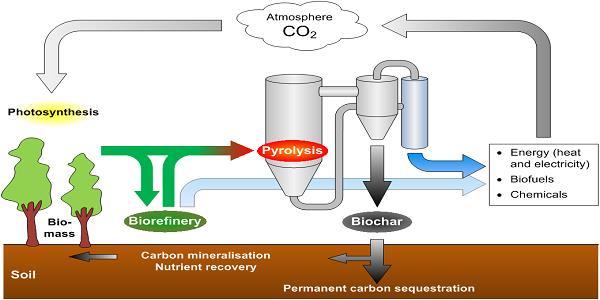
A comprehensive understanding of the conversion processes is essential for harnessing biomass energy efficiently:
- Combustion: Biomass materials are burned to produce heat, which can be used to generate steam and drive turbines for electricity production.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a combustible gas mixture called syngas, which can be used to generate electricity or produce biofuels.
- Pyrolysis: Biomass materials are subjected to high temperatures in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of bio-oils, gases, and char, which can be further processed for energy applications.
These processes enable the efficient utilization of biomass resources and contribute to sustainable energy production.
2. What are the sources of biomass?
Biomass can be derived from various sources, including:

- Forestry Residues: Wood chips, bark, sawdust, and tree trimmings left after logging or forest management activities.
- Agricultural Biomass: Crop residues, such as corn stalks, wheat straw, rice husks, and sugarcane bagasse.
- Energy Crops: Dedicated energy crops, like switchgrass and miscanthus, grown specifically for biomass energy production.
- Algae: Microalgae cultivated in large-scale ponds or photobioreactors, which can be converted into biofuels.
- Organic Waste: Municipal solid waste, food wastes, and animal manure can be processed to extract energy-rich biogas through anaerobic digestion.
These biomass sources provide renewable and sustainable feedstocks for energy generation, offering a valuable alternative to fossil fuels.
3. What are the environmental benefits of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several environmental advantages:
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: Biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral, as the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed by plants during their growth. This helps mitigate climate change and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste Reduction: Utilizing agricultural and organic waste as biomass feedstocks helps divert these materials from landfills and reduces pollution risks associated with their disposal.
- Renewable Resource: Biomass is a renewable energy source, as plants can be regrown and waste materials continuously generated.
- Local Economic Development: Biomass energy projects can contribute to job creation in rural areas, stimulate local economies, and reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels.
These benefits make biomass energy a promising sustainable energy solution with positive environmental impacts.
4. Can biomass energy help reduce reliance on fossil fuels?
Yes, biomass energy can play a vital role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels. As a renewable energy source, biomass offers a sustainable alternative to non-renewable and finite fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. By utilizing biomass, we can diversify our energy mix and decrease dependence on fossil fuel imports. However, it is important to ensure sustainable biomass practices that protect ecosystems, maintain soil health, and avoid competition with food production.
5. How does biomass energy compare to other renewable energy sources?
Biomass energy has several advantages compared to other renewable energy sources:
- Reliable and Storable: Biomass can be stored for later use, providing a reliable and flexible energy supply, unlike some intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind.
- Dispatchable Power: Biomass power plants can be operated on demand, allowing for grid stability and meeting base-load electricity demands.
- High Energy Density: Biomass has a higher energy density compared to wind or solar energy, making it suitable for applications requiring concentrated energy, such as industrial processes and transportation.
- Economic Opportunities: Biomass cultivation, processing, and utilization can create jobs and contribute to regional economic growth.
However, it is important to consider the specific context and regional resources when comparing biomass energy to other renewables, as each energy source has its own strengths and limitations.
6. What are the challenges associated with biomass energy?
While biomass energy offers numerous benefits, certain challenges exist:
- Feedstock Availability: Ensuring a consistent and sustainable biomass supply can be challenging, requiring efficient feedstock logistics and suitable biomass cultivation practices.
- Emissions and Air Quality: Improper combustion or lack of emission controls in biomass facilities can lead to air pollution, emphasizing the importance of proper emissions management.
- Land Use Impacts: Expanding biomass cultivation may encroach upon ecologically valuable land or compete with food production, demanding careful land use planning and sustainable practices.
- Technological Advances: Further research and development are needed to improve conversion technologies, increase energy efficiencies, and optimize biomass utilization.
Addressing these challenges is crucial to maximizing the potential of biomass energy and ensuring its long-term sustainability.
7. What are the main bioenergy conversion processes?
Bioenergy conversion involves various processes to transform biomass into usable energy forms:
- Combustion: The most straightforward conversion process where biomass is burned to generate heat or produce steam, which drives turbines for electricity production.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a combustible gas mixture called syngas, composed mainly of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane. This syngas can be used for electricity generation, as a heat source, or further refined into biofuels.
- Pyrolysis: Biomass is decomposed by heat in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the formation of bio-oil, syngas, and char. Bio-oil can be used as a feedstock for biofuels or as a source of chemicals, while syngas can be utilized for heat and power generation.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Organic waste materials undergo a biochemical process in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas rich in methane and carbon dioxide. This biogas can be used directly for heating, electricity production, or upgraded to biomethane for injection into gas grids or transportation fuel.
These conversion processes offer versatile options for harnessing the energy potential of biomass.
8. How does biomass energy contribute to sustainable agriculture?
Integrating biomass energy systems into agriculture can provide several sustainability benefits:
- Waste Utilization: By utilizing agricultural residues and organic waste, biomass energy reduces the need for waste disposal while utilizing these materials' energy content.
- Soil Health: Certain biomass crops, like switchgrass, can improve soil quality by enhancing nutrient cycling, reducing erosion, and increasing organic matter content.
- Crop Rotation and Sustainability: Biomass energy systems can be integrated into crop rotation practices, promoting sustainable land management and diversifying income sources for farmers.
- Improved Resilience: Biomass energy allows farmers to have multiple sources of income and reduces their dependence on traditional commodity markets, providing greater resilience in fluctuating agricultural markets.
These sustainable agriculture benefits contribute to the overall environmental and economic sustainability of biomass energy.
9. Can biomass energy be used for transportation?
Yes, biomass energy can be used for transportation through the production of biofuels:
- Bioethanol: Produced by fermenting biomass, such as corn or sugarcane, bioethanol is commonly blended with gasoline and used as a transportation fuel. It is primarily utilized in flex-fuel vehicles and has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Biodiesel: Derived from vegetable oils, animal fats, or used cooking grease, biodiesel is used as a replacement for or blend with conventional diesel fuel. Biodiesel reduces carbon emissions and provides lubricity and other benefits to diesel engines.
- Biogasoline: Produced through the gasification and catalytic conversion of biomass, biogasoline has similar properties to conventional gasoline and can be used as a drop-in fuel substitute.
These biofuels offer greener alternatives to conventional fossil fuels, contributing to reducing transportation sector emissions.
10. What role does government policy play in promoting biomass energy?
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting the development and adoption of biomass energy:
- Renewable Energy Standards: Governments can set targets for renewable energy generation, including biomass, to encourage utilities and energy producers to invest in and develop biomass-based projects.
- Feed-in Tariffs: Offering stable and long-term electricity price agreements, feed-in tariffs incentivize biomass power producers and provide financial support for the generation of renewable energy from biomass.
- Tax Credits and Grants: Governments can provide tax credits or grants to support the adoption of biomass energy systems, such as biomass heating systems for residential or commercial use.
- Research and Development Funding: Governments can allocate funding to support research and development initiatives aimed at improving biomass conversion technologies, enhancing efficiency, and optimizing biomass resource utilization.
These policies create a favorable environment for the growth of biomass energy and help drive the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
11. What are some successful case studies of biomass energy implementation?
Several successful case studies demonstrate the effective implementation of biomass energy:
- Denmark: Denmark has successfully utilized biomass for district heating, providing renewable heat to communities. Biomass accounts for a significant share of their renewable energy mix.
- Sweden: Sweden has made significant strides in biomass district heating and bioenergy production. They have effectively utilized biomass residues and forest biomass to generate heat and electricity.
- United States: Many states in the US have implemented biomass co-firing in coal power plants, substituting a portion of coal with biomass to reduce carbon emissions and diversify energy sources.
- Germany: Germany has emerged as a leader in biogas production from organic waste through anaerobic digestion. They have successfully integrated biogas into their energy mix and are exploring innovative uses such as biogas upgrading and injection into the natural gas grid.
These case studies highlight the successful implementation of biomass energy in various contexts and underline its potential for sustainable energy production.
12. How can individuals contribute to the adoption of biomass energy?
Individuals can contribute to the adoption of biomass energy in several ways:
- Promote Awareness: Spread the word about biomass energy and its benefits to raise awareness among friends, family, and the wider community. Educate others about the potential of biomass as a renewable energy source.
- Support Local Projects: Get involved in local biomass energy projects, support initiatives that promote the use of biomass, and advocate for government policies that incentivize biomass energy adoption.
- Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-efficient practices in homes and businesses to reduce overall energy consumption, creating a greater demand for renewable energy sources like biomass.
- Waste Management: Practice responsible waste management by recycling, composting, or supporting community initiatives for organic waste collection. This ensures the availability of feedstock for biomass energy production.
By taking on these actions, individuals can contribute to a sustainable energy future and help drive the adoption of biomass energy on a broader scale.