how much energy is produced by biomass
Types of Biomass
Biomass refers to any organic matter derived from plants, animals, or microorganisms that can be used as a renewable energy source. It plays a significant role in the sustainable energy sector. In this article, we will explore the different types of biomass and their importance in the field of bioenergy.
1. What is biomass?
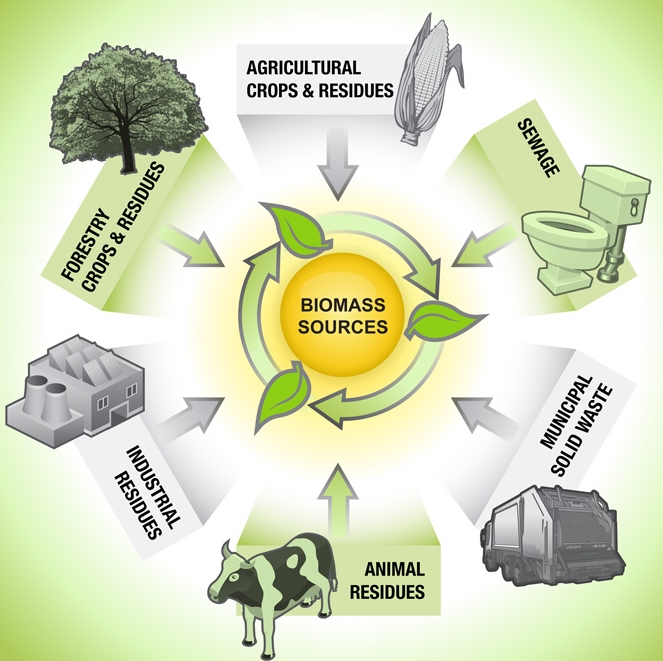
Biomass refers to any organic matter derived from plants, animals, or microorganisms that can be used as a renewable energy source. It includes various materials such as agricultural crops, forestry residues, animal waste, and dedicated energy crops.
- Biomass is a key component in the production of bioenergy and can be converted into various forms such as solid biomass, liquid biofuels, and biogas.
- It is a renewable energy source as it relies on the continuous growth and replenishment of organic materials.
- Biomass energy production leads to reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
2. What are the different types of biomass?
There are several types of biomass that can be utilized for energy production:
- Woody Biomass: This includes wood from forests, tree plantations, and wood processing residues. It is commonly used for heating, electricity generation, and production of biofuels.
- Agricultural Biomass: This includes crop residues, animal manure, and dedicated energy crops such as switchgrass and miscanthus. It can be converted into biofuels, biogas, and used for heat and power production.
- Energy Crops: These are specifically grown crops, such as corn, sugarcane, and oil palm, that are cultivated for their high energy content. They are used primarily for biofuel production.
- Algae: Algae are versatile sources of biomass that can be cultivated in various aquatic environments. They can be converted into biofuels and other high-value products.
- Municipal Solid Waste: Organic waste from households and industries can be processed to extract biogas through anaerobic digestion.
Each type of biomass has its own unique characteristics and applications in the field of bioenergy.
3. How is biomass converted into energy?
Biomass can be converted into energy through various processes:
- Combustion: Biomass is burned to produce heat, which can be used for space heating, water heating, or electricity generation through steam turbines.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Organic materials, such as animal manure and crop residues, are decomposed by bacteria in oxygen-free conditions, producing biogas that can be utilized for heat and power production.
- Biochemical Conversion: Biomass is broken down into sugars, which can be fermented to produce biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel.
- Thermochemical Conversion: Biomass is subjected to high temperatures in the absence of oxygen to produce syngas, which can be used as a fuel for combustion engines or converted into various liquid and gaseous biofuels.
These conversion processes play a vital role in harnessing the energy potential of biomass.
4. What are the advantages of using biomass for energy?
Utilizing biomass for energy offers several benefits:
- Renewable Energy Source: Biomass is derived from organic materials, which can be continuously replenished, making it a sustainable and renewable energy source.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biomass energy production leads to lower net emissions of greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuels, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Waste Management: Biomass can be derived from agricultural residues, forestry waste, and organic waste streams, providing an opportunity for effective waste management and reducing environmental pollution.
- Regional Development: Biomass resources are often locally available, promoting regional economic development and reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
These advantages make biomass a valuable alternative to fossil fuels in achieving a sustainable energy future.
5. What are the challenges associated with biomass energy?
While biomass energy offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges that need to be addressed:
- Sustainable Resource Management: Biomass resources need to be harvested and managed sustainably to prevent negative impacts on ecosystems, biodiversity, and food security.
- Efficiency and Cost: Biomass energy conversion processes can be less efficient and more costly compared to conventional fossil fuel-based technologies, requiring ongoing research and development efforts.
- Competition for Resources: The use of biomass for energy production can compete with other important sectors such as agriculture and forestry, highlighting the need for careful resource allocation and planning.
- Environmental Impacts: Biomass production and conversion processes can have environmental impacts such as soil degradation, water pollution, and air emissions. These impacts need to be carefully managed to ensure sustainability.
Addressing these challenges will be crucial in maximizing the potential benefits of biomass energy.
Facts Everyone Should Know About Renewable Electricity Market In India

The renewable electricity market in India has witnessed significant growth in recent years. With the country's commitment to reducing carbon emissions and increasing energy access, renewable energy sources have become a crucial part of India's energy landscape. In this article, we will explore some key facts about the renewable electricity market in India and its impact on the country's energy transition.
1. How has the renewable electricity market grown in India?
The renewable electricity market in India has experienced tremendous growth over the past decade:
- Installed Capacity: India has become one of the world's largest renewable energy producers, with a total installed capacity of over 92 gigawatts (GW) as of 2021.
- Solar Power: Solar energy has seen significant growth, with India emerging as one of the leading countries in solar photovoltaic (PV) installations.
- Wind Power: India has a substantial wind power capacity, ranking fourth globally in terms of installed wind power capacity.
- Policy Support: The Indian government has implemented various policies and incentives to promote renewable energy, such as the National Solar Mission and Renewable Purchase Obligations.
This growth in the renewable electricity market reflects India's commitment to a sustainable energy future.
2. What are the key drivers behind India's renewable energy growth?
There are several factors driving the growth of renewable energy in India:
- Government Policies: The Indian government has introduced supportive policies and initiatives to encourage renewable energy deployment, including feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and renewable energy targets.
- Declining Costs: The cost of renewable energy technologies, especially solar and wind, has declined significantly in recent years. This has made renewable energy more competitive with conventional fossil fuel-based sources.
- Energy Security: India, as a rapidly developing nation, aims to reduce its dependence on fossil fuel imports and enhance its energy security by diversifying its energy sources through renewable energy.
- Environmental Benefits: Renewable energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and mitigate the impacts of climate change, which are significant priorities for India.
These factors have created a conducive environment for the growth of renewable electricity in India.
3. What are the challenges in the renewable electricity market in India?
While the renewable electricity market in India shows promising growth, it also faces several challenges:
- Intermittency: Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind are intermittent in nature, with variations in generation based on weather conditions. This poses challenges for grid integration and balancing power supply and demand.
- Grid Infrastructure: India's grid infrastructure needs to be upgraded to accommodate the increasing penetration of renewable energy sources and ensure reliable and stable electricity supply.
- Financial Viability: Although the cost of renewable energy technologies has decreased, project financing and ensuring economic viability remain significant challenges.
- Land and Resource Availability: Acquiring land for renewable energy projects and ensuring a sustainable supply of resources such as biomass and hydropower can be complex and time-consuming.
Addressing these challenges will be crucial for further scaling up renewable electricity in India.
4. What are the benefits of renewable electricity in India?
Renewable electricity offers numerous benefits for India:
- Clean and Sustainable Energy: Renewable electricity sources help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and contribute to India's sustainable development goals.
- Energy Access: Renewable energy can provide electricity access to remote and rural areas, where grid infrastructure is limited or unavailable.
- Job Creation: The renewable electricity sector has the potential to generate employment opportunities, both in the installation and operation of renewable energy projects.
- Energy Independence: Investing in renewable energy reduces India's dependence on imported fossil fuels, promoting energy independence and enhancing energy security.
These benefits align with India's vision of achieving a clean, affordable, and reliable energy future.
5. What are the future prospects for renewable electricity in India?
The future prospects for renewable electricity in India are promising:
- Solar Power Growth: India has ambitious plans to expand its solar power capacity, aiming for 100 GW of solar installations by 2022.
- Wind Power Potential: India has vast wind power potential, especially in coastal regions and states like Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, which can further contribute to renewable electricity growth.
- Battery Storage: The development of energy storage technologies, especially battery storage, can help mitigate intermittency challenges and enable higher renewable energy integration.
- Policy Support: The Indian government continues to introduce policies and regulatory frameworks to support renewable energy deployment and attract investments.
With continued support and investment, the renewable electricity market in India has the potential to revolutionize the country's energy sector.