how is biomass used to generate energy
Biomass Energy: An Introduction and Sources
Question 1: What is biomass energy?
Biomass energy is a renewable source of energy derived from organic matter, such as plants, crops, wood, and agricultural waste. It can be used to generate heat, electricity, or as a fuel for vehicles.
Question 2: Where does biomass come from?

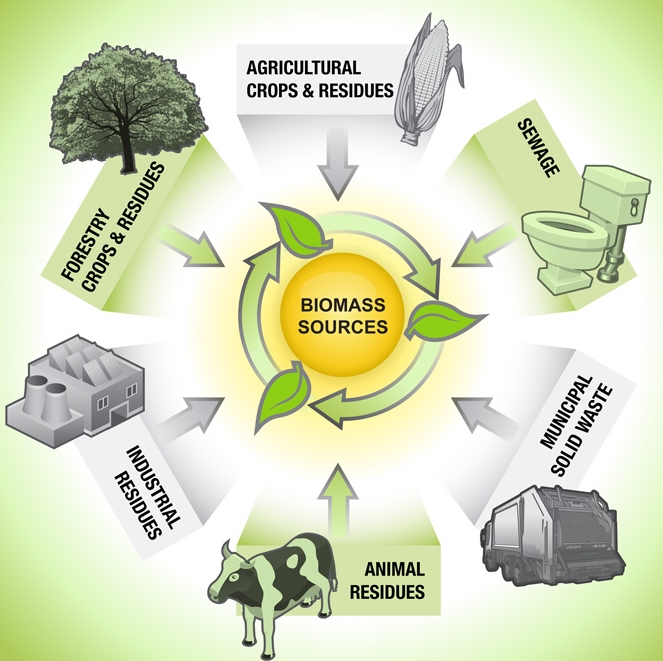
Biomass can come from various sources, including:
- Forest residues
- Agricultural residues
- Energy crops
- Algae
- Animal manure
- Urban waste
Question 3: What are the benefits of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several benefits, including:
- Renewability: Biomass is a renewable energy source as new plants and crops can be grown to replace the ones used for energy production.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy releases carbon dioxide during combustion, but this can be offset by the carbon absorbed during the growth of new plants, making it carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative.
- Waste management: Utilizing biomass for energy helps reduce the amount of agricultural waste and forest residues that would otherwise be burned or discarded.
- Diversification of energy sources: Biomass energy offers an alternative to finite fossil fuels, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
Question 4: How is biomass energy converted into electricity?
Biomass can be converted into electricity through various processes:
- Combustion: Biomass is burned to produce steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a gas (syngas) through a high-temperature process, and the gas is then used to power a turbine.
- Anaerobic digestion: Biomass, particularly organic waste, can be decomposed by bacteria in the absence of oxygen to produce methane gas, which can be used for electricity generation.
Question 5: Is biomass energy sustainable?
Biomass energy has the potential to be sustainable if managed properly. Sustainable practices include:
- Using energy crops that can be grown on marginal lands without competing with food production.
- Implementing efficient technologies to minimize resource use and maximize energy output.
- Promoting responsible forest management to ensure a continuous supply of wood-based biomass.
Question 6: What are the challenges of using biomass energy?
Despite its advantages, biomass energy also faces some challenges:
- Competition for land: Growing energy crops for biomass production may compete with land used for food production or natural ecosystems.
- Transportation and logistics: Biomass materials need to be collected, transported, and stored before they can be used, which can be logistically challenging and costly.
- Emissions: Inefficient combustion or inadequate pollution controls during biomass combustion can lead to emissions of pollutants like particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds.
- Supply chain management: Biomass availability can vary seasonally and regionally, necessitating a well-managed supply chain to ensure a continuous and reliable supply of feedstock.
Question 7: Can biomass energy help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
Biomass energy can potentially help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. While the combustion of biomass does release carbon dioxide, the CO2 emitted is roughly equal to the carbon absorbed by the plants during their growth phase. This makes biomass energy carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative in some cases. By displacing fossil fuels, biomass energy can contribute to reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Question 8: How does biomass energy compare to fossil fuels?
Biomass energy differs from fossil fuels in several ways:
- Renewability: Biomass is derived from organic matter that can be regrown, making it renewable, while fossil fuels are formed from ancient organic matter and are non-renewable.
- Carbon footprint: Biomass energy can be carbon-neutral or carbon-negative, as the carbon emitted during combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed during plant growth; fossil fuels release stored carbon, contributing to increased greenhouse gas levels.
- Availability: Fossil fuels are finite resources, while biomass can be continually produced on an ongoing basis.
- Emissions: Biomass combustion generally produces lower levels of sulfur and nitrous oxides compared to fossil fuels, helping reduce air pollution.
Question 9: How can households benefit from biomass energy?
Households can benefit from biomass energy in various ways:
- Heating: Biomass-based heating systems, such as pellet stoves or boilers, can provide efficient and cost-effective heating for homes.
- Electricity generation: Small-scale biomass power plants can be installed to generate electricity for individual households or communities.
- Hot water production: Biomass can be utilized in water heaters to provide hot water for domestic use.
- Cooking: Biomass cookstoves can be used for cooking and can be a viable alternative in areas without access to gas or electricity.
Question 10: Are there any limitations to biomass energy?
There are a few limitations to consider when it comes to biomass energy:
- Resource availability: The availability of biomass resources can vary geographically and seasonally, which may pose challenges in ensuring a consistent supply.
- Investment costs: Establishing biomass power plants or other energy systems can require significant upfront investment, making it economically challenging for some regions or individuals.
- Conversion efficiency: The conversion of biomass into energy is not as efficient as burning fossil fuels, resulting in lower energy output for the same amount of fuel.
- Environmental impact: Poorly managed biomass cultivation or inefficient combustion can have negative environmental impacts, such as habitat destruction or increased emissions.
Question 11: Is biomass energy cost-effective?
The cost-effectiveness of biomass energy depends on various factors:
- Resource availability: Biomass availability in the region and proximity to energy consumers can affect transportation costs and overall feasibility.
- Economies of scale: Large-scale biomass power plants may benefit from economies of scale, reducing the cost of electricity production.
- Government incentives: Financial incentives and supportive policies, such as feed-in tariffs or tax credits, can improve the cost-effectiveness of biomass energy.
- Technology advancements: Continuous improvements in biomass conversion technologies can increase efficiency and lower costs over time.
Question 12: Can biomass energy be used in transportation?
Biomass energy can indeed be used in transportation:
- Biofuels: Biomass can be converted into liquid transportation fuels, such as ethanol or biodiesel, that can be used as alternatives to gasoline or diesel.
- Biogas: Biomass, particularly organic waste, can be anaerobically digested to produce methane gas, which can be used as a fuel for vehicles.
- Advanced biofuels: Researchers are exploring advanced biofuels made from non-food crops or agricultural residues that have the potential to be used as drop-in replacements for conventional fuels.