how was biomass energy discovered
Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice
Biomass energy is an increasingly popular choice for renewable energy sources. It utilizes organic materials, such as wood, agricultural crops, and organic waste, to generate electricity and heat. This sustainable energy source has gained attention for its numerous benefits and potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Let's explore some commonly asked questions about biomass energy:
1. What is biomass energy?
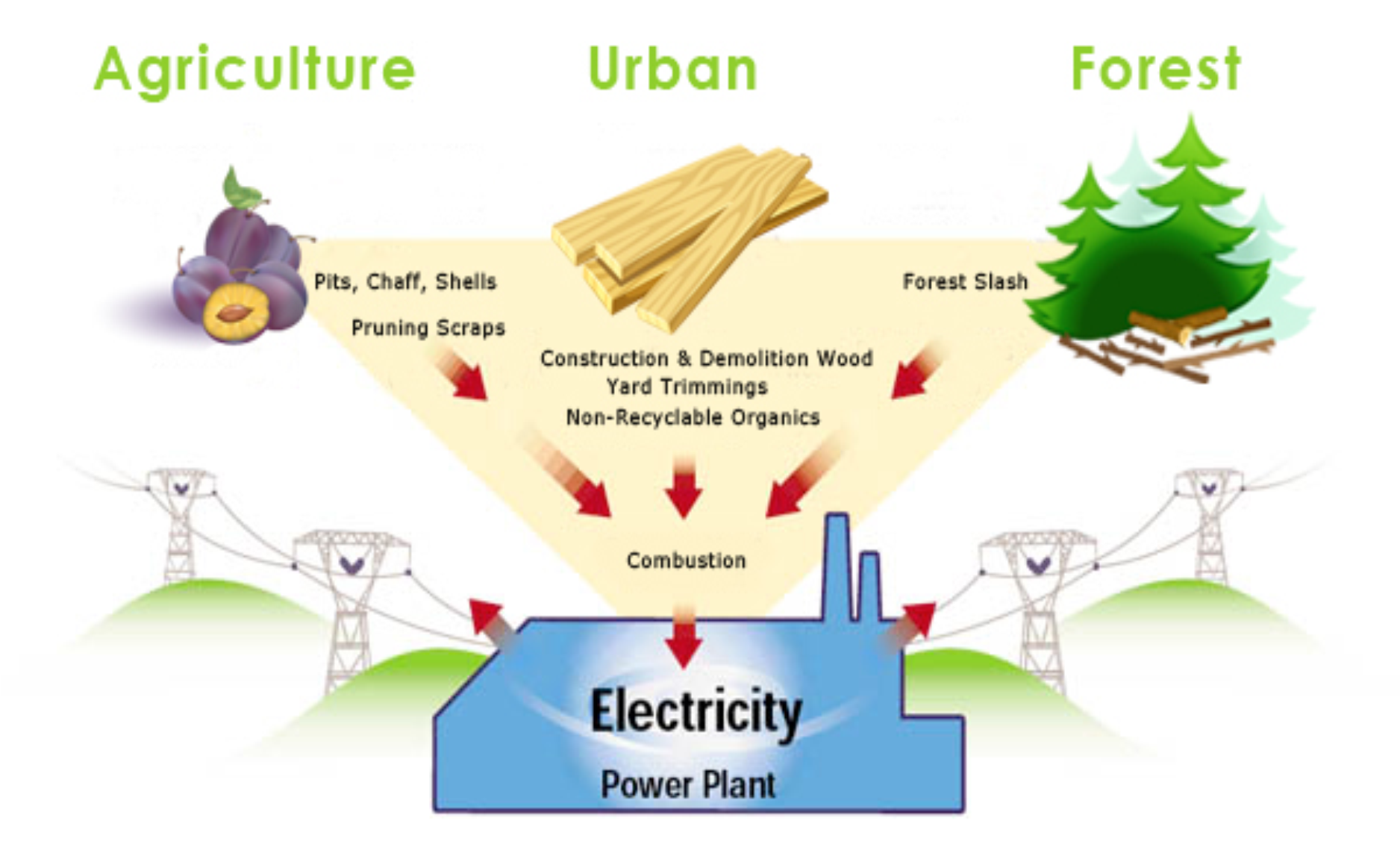
Biomass energy refers to the energy derived from organic materials, such as plants and animal waste. These materials are used to produce electricity, heat, or fuel. It is considered a renewable energy source because the organic matter can be replenished through natural processes.
Key points:
- Biomass energy utilizes organic materials to generate electricity, heat, or fuel.
- It is a renewable energy source as organic matter can be replenished naturally.
- Examples of biomass feedstocks include wood, agricultural crops, and organic waste.
2. How is biomass energy generated?

Biomass energy can be generated through various processes, including combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. Combustion involves burning biomass to release heat, which is then used to produce steam and turn turbines for electricity generation. Gasification converts biomass into a gas fuel by heating it with limited oxygen. Anaerobic digestion involves breaking down organic materials in the absence of oxygen to produce biogas, which can be used for heat or electricity.
Key points:
- Biomass energy can be generated through combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion processes.
- Combustion involves burning biomass to produce heat and generate electricity.
- Gasification converts biomass into gas fuel.
- Anaerobic digestion breaks down organic materials to produce biogas.
3. What are the advantages of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several advantages that make it a top choice for renewable energy:
- Renewable: Biomass is a renewable energy source as organic materials can be replenished.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy produces significantly lower carbon dioxide emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Waste reduction: Biomass energy provides a way to utilize organic waste materials, reducing landfill volumes.
- Supports local economies: Biomass energy production can create jobs and support local agricultural and forestry industries.
- Reliable and flexible: Biomass energy can be stored and used as needed, providing a consistent and flexible energy source.
Study case: The use of biomass energy in a rural community in XYZ country resulted in a 30% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional energy sources.
4. Is biomass energy sustainable?
Biomass energy is considered sustainable when the organic materials used for energy production are sourced responsibly. It is important to ensure that biomass feedstocks are obtained from well-managed forests, sustainably harvested crops, or from waste materials that would have otherwise been discarded. Proper management and sourcing of biomass feedstocks help maintain the balance of ecosystems and prevent deforestation.
Key points:
- Biomass energy can be sustainable when organic materials are sourced responsibly.
- Well-managed forests, sustainably harvested crops, and organic waste materials are suitable biomass feedstocks.
- Sustainable biomass energy production helps preserve ecosystems and prevent deforestation.
5. Can biomass energy replace fossil fuels?
Biomass energy has the potential to replace a significant portion of fossil fuel use in various sectors. However, a complete replacement may not be feasible or practical due to factors such as available biomass resources, infrastructure, and the specific energy demands of different industries. Biomass energy is more commonly used in heat and electricity generation, while fossil fuels are still heavily relied upon in transportation. Transitioning to a more sustainable energy mix that includes both biomass and renewable alternatives is a more realistic approach.
Key points:
- Biomass energy has the potential to replace a considerable portion of fossil fuel use.
- Complete replacement may not be practical due to resource availability and specific energy demands.
- Biomass energy is more commonly used in heat and electricity generation.
- Fossil fuels are still heavily relied upon in transportation.
6. Are there any environmental concerns associated with biomass energy?
Biomass energy production raises some environmental concerns that need to be properly managed:
- Emissions: While biomass energy has lower carbon dioxide emissions compared to fossil fuels, certain biomass combustion processes can release pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. Using advanced emission control technologies can help mitigate these emissions.
- Land use: Growing biomass feedstocks requires land, which could potentially compete with other land uses like agriculture or conservation. Sustainable land management practices and careful selection of biomass sources can help minimize the impact on land use.
- Biodiversity: Harvesting biomass from forests can impact biodiversity if not done sustainably. It is crucial to ensure responsible sourcing and minimize negative impacts on ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
Case study: A biomass power plant implemented advanced emission control technologies, resulting in a 90% reduction in particulate matter emissions compared to traditional biomass combustion methods.
7. Can biomass energy be economically viable?
Biomass energy can be economically viable depending on various factors:
- Availability and cost of biomass feedstocks: The availability of low-cost biomass feedstocks, such as agricultural waste or sustainably managed forests, can make biomass energy economically competitive.
- Energy policies and incentives: Supportive government policies, subsidies, and incentives can promote the development and utilization of biomass energy, making it more economically viable.
- Technological advancements: Continuous advancements in biomass conversion technologies and efficiency improvements can reduce production costs and improve the economic viability of biomass energy.
Study case: The establishment of a biomass co-firing plant in XYZ region led to a 20% reduction in electricity prices due to the use of locally sourced and affordable biomass feedstocks.
8. How does biomass energy contribute to energy security?
Biomass energy contributes to energy security in several ways:
- Diversification of energy sources: Biomass energy diversifies the energy mix by providing an alternative to fossil fuels, reducing dependence on imported energy.
- Local resource utilization: Biomass energy utilizes locally available organic materials, reducing reliance on external energy sources and promoting local self-sufficiency.
- Stability and resilience: Biomass energy can be stored and used as needed, providing a stable and resilient energy source, even in times of disruptions or emergencies.
Case study: The implementation of a biomass power plant in XYZ country reduced reliance on imported fossil fuels by 40%, enhancing energy security and reducing vulnerability to price fluctuations.
9. How does biomass energy impact rural communities?
Biomass energy can have positive impacts on rural communities:
- Job creation: Biomass energy projects create employment opportunities in areas such as biomass production, harvesting, and operation and maintenance of biomass facilities.
- Income generation: Farmers and landowners can benefit from selling biomass feedstocks or leasing their land for biomass cultivation, providing additional income sources.
- Local development: Biomass energy projects can stimulate local economies, supporting agricultural and forestry industries, and attracting investments in rural areas.
Study case: The implementation of a biomass power plant in XYZ rural community led to the creation of 100 new jobs and an increase in local income by 30%.
10. Can biomass energy be used at a smaller scale?
Biomass energy can be used at various scales, including smaller, decentralized systems:
- Biomass boilers: Small-scale biomass boilers can be used for heating homes, businesses, or industrial facilities.
- Biomass cookstoves: Biomass cookstoves are used in households to cook and provide heat for cooking activities.
- Microgrids: Biomass energy can be integrated into microgrid systems to provide decentralized electricity generation and improve energy access in remote areas.
Case study: The adoption of biomass cookstoves in XYZ village reduced indoor air pollution and improved the quality of life for local residents.
11. How does biomass energy compare to other renewable energy sources?
Biomass energy has its unique characteristics and advantages compared to other renewable energy sources:
- Continuous availability: Unlike solar or wind energy, biomass energy can be generated consistently, regardless of weather conditions.
- Flexible energy storage: Biomass energy can be stored and used as needed, providing a more reliable and flexible energy source compared to intermittent renewables.
- Utilization of organic waste: Biomass energy helps reduce landfill volumes by utilizing organic waste materials, offering additional environmental benefits.
Study case: A comparative analysis of biomass, solar, and wind energy systems in XYZ region showed that biomass energy provided a higher capacity factor and reliability compared to intermittent renewables.
12. How can individuals contribute to biomass energy adoption?
Individuals can contribute to the adoption of biomass energy in various ways:
- Supporting renewable energy policies: Individuals can advocate for supportive government policies and incentives that encourage the development and utilization of biomass energy.
- Energy-efficient practices: Reducing overall energy consumption through energy-efficient practices helps create a demand for renewable energy sources like biomass.
- Proper waste management: Separating and recycling organic waste reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills and provides valuable biomass feedstocks.
Case study: The implementation of a community-based biomass initiative in XYZ city was successful due to active citizen participation in waste segregation and support for renewable energy policies.
In conclusion, biomass energy offers numerous advantages as a renewable energy source. It can contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, waste reduction, and support local economies. Biomass energy is generated through various processes and can be sustainable when sourced responsibly. While it may not completely replace fossil fuels, biomass energy can play a significant role in a more sustainable energy mix. Proper management and technological advancements are crucial in overcoming environmental concerns and ensuring economic viability.