how is biomass used to create energy
Types of Biomass
Types of Biomass | BioEnergy Consult
1. What is biomass? How is it different from other energy sources?
Biomass refers to any organic matter derived from plants, animals, or microorganisms that can be used as a renewable source of energy. Unlike fossil fuels, which are formed from ancient organic materials over millions of years, biomass is a sustainable and readily available resource.
An expert would provide a more detailed explanation, including examples of biomass sources such as agricultural residues, forestry wastes, and energy crops.
- Examples of biomass sources
- Comparison of biomass with fossil fuels
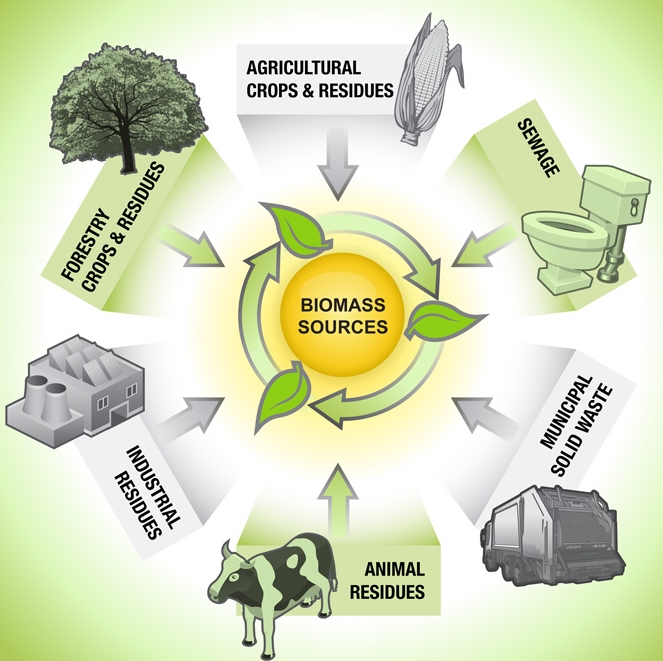
2. What are the different types of biomass?
There are several types of biomass, including:
- Wood and wood waste
- Agricultural crops and residues
- Algae
- Animal manure and residues
- Food processing wastes
An expert would elaborate on each type of biomass, discussing their characteristics and potential applications.
- Characteristics of different types of biomass
- Potential applications of each biomass type
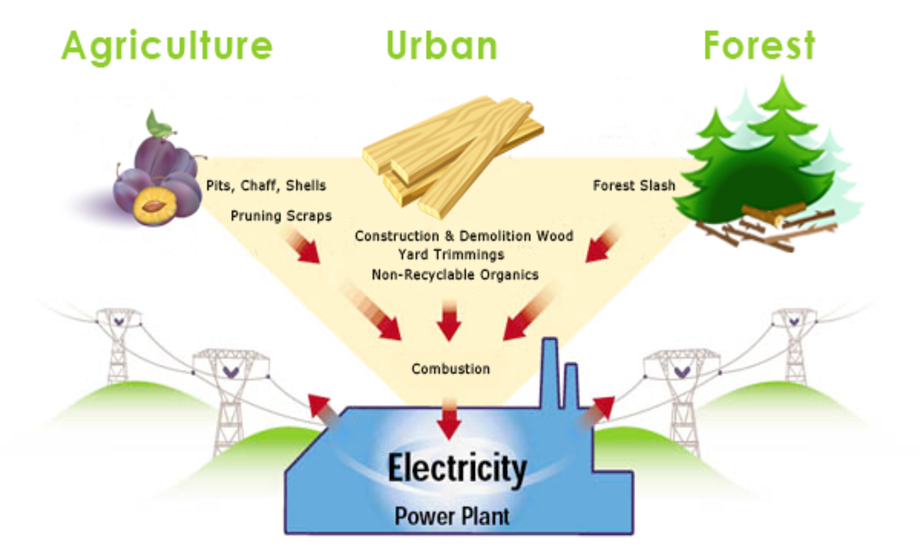
3. How is biomass used as an energy source?
Biomass can be converted into various forms of energy, including:
- Biofuels: Biomass can be processed into liquid or gaseous fuels, such as bioethanol or biogas, which can be used for transportation or heating purposes.
- Biomass power plants: Biomass can be burned to generate electricity and heat in specialized power plants.
- Biomass co-firing: Biomass can be mixed with coal in existing coal-fired power plants to reduce carbon emissions.
An expert would provide a more comprehensive explanation, discussing the advantages and challenges of each biomass conversion method.
- Advantages of using biomass as an energy source
- Challenges and limitations of biomass conversion
4. What are the environmental benefits of using biomass as an energy source?
Using biomass as an energy source offers several environmental benefits, such as:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but the carbon dioxide is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed during the growth of biomass feedstocks.
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: Biomass provides an alternative to fossil fuels, reducing our dependence on non-renewable resources.
- Waste reduction: Biomass energy can be derived from agricultural and forestry waste, reducing the need for disposal and preventing methane emissions from decomposing organic matter.
An expert would provide further insights on the environmental advantages, discussing the potential for carbon neutrality and sustainable land management through biomass utilization.
- Potential for carbon neutrality
- Sustainable land management through biomass utilization
Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice
Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice - REURASIA
5. What are the key advantages of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several key advantages, including:
- Renewable and sustainable: Biomass is derived from organic matter that can be replenished, making it a renewable energy source.
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but the overall emissions are balanced by CO2 absorption during biomass growth.
- Job creation and economic benefits: Biomass industries create jobs in biomass cultivation, processing, and conversion.
An expert would delve into each advantage, providing data and examples to support the claims.
- Statistics on job creation in the biomass sector
- Case studies on economic benefits derived from biomass energy
6. How does biomass energy contribute to waste management?
Biomass energy plays a significant role in waste management by:
- Utilizing agricultural and forestry residues: Biomass energy systems can incorporate waste materials that would otherwise be discarded, reducing waste and associated environmental impacts.
- Converting organic waste into energy: Biomass can be used to generate energy from organic waste streams, such as food processing waste or animal manure.
An expert would further discuss the benefits of waste-to-energy conversion using biomass, highlighting case studies and technological advancements.
- Case studies on successful waste-to-energy projects
- Technological advancements in biomass waste conversion
7. Can biomass energy support rural development?
Yes, biomass energy has the potential to support rural development in multiple ways:
- Job creation: Biomass cultivation, harvest, and processing can provide employment opportunities in rural areas.
- Local resource utilization: Biomass energy allows rural communities to harness their local resources, promoting self-reliance and reducing dependence on external energy sources.
- Income generation: Biomass energy can create income streams for farmers by utilizing their agricultural residues or growing energy crops.
An expert would elaborate on these points, providing case studies and examples showcasing the positive impact of biomass energy on rural communities.
- Case studies on rural development through biomass energy
- Success stories of income generation from biomass utilization
8. What are the challenges associated with biomass energy?
Biomass energy also faces several challenges, such as:
- Feedstock availability and quality: Sufficient biomass feedstock must be available at a reasonable cost, and its quality should meet the requirements of the conversion process.
- Logistics and transportation: Biomass feedstock often requires transportation over long distances, which can be costly and environmentally challenging.
- Technological limitations: Biomass conversion technologies require continuous innovation to improve efficiency and address specific feedstock characteristics.
An expert would provide a comprehensive analysis of these challenges, discussing ongoing research and potential solutions.
- Ongoing research in feedstock improvement
- Innovations in biomass transportation and logistics
- New technologies addressing biomass conversion limitations
9. How does biomass energy compare to other renewable energy sources?
When compared to other renewable energy sources like solar or wind, biomass energy has its unique advantages:
- Continuous availability: While solar and wind energy are intermittent, biomass energy can be produced consistently, providing a stable power supply.
- Dispatchability: Biomass power plants can be dispatched according to demand, making them reliable for baseload or peak load electricity generation.
- Economic feasibility: Biomass energy can often be produced at a lower cost compared to some other renewable options.
An expert would offer a comprehensive comparison, considering factors such as environmental impact, scalability, and technological maturity.
- Life cycle analysis comparing different renewable energy sources
- Technological advancements and potential integration of biomass with other renewables
10. Is biomass energy financially viable?
Yes, biomass energy can be financially viable under the right circumstances:
- Economies of scale: Large-scale biomass power plants can benefit from economies of scale, reducing the cost per unit of energy produced.
- Government incentives and policies: Supportive policies, such as feed-in tariffs or tax incentives, can enhance the financial viability of biomass energy projects.
- Co-generation and waste heat utilization: Efficient utilization of waste heat or combined heat and power (CHP) systems can improve the overall financial performance of biomass energy projects.
An expert would provide further insights into the financial aspects of biomass energy, discussing investment considerations and potential returns on investment.
- Case studies on successful and financially viable biomass energy projects
- Analysis of government policies and incentives supporting biomass energy
11. What is the future outlook for biomass energy?
The future of biomass energy looks promising, with several factors driving its growth:
- Increasing renewable energy targets: Many countries have set ambitious renewable energy targets, creating a demand for biomass as a sustainable energy source.
- Technological advancements: Ongoing research and development are improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biomass conversion technologies.
- Integration with other sectors: Biomass energy can be integrated with sectors like agriculture, forestry, and waste management, creating synergies and maximizing the utilization of resources.
An expert would provide a vision for the future of biomass energy, discussing potential trends, innovations, and policy developments.
- Potential biomass energy market growth
- Emerging technologies and their impact on the biomass sector
12. How can individuals contribute to the development of biomass energy?
Individuals can contribute to the development of biomass energy in various ways:
- Supporting renewable energy policies: Advocate for policies that promote the development and utilization of biomass energy at local, national, and international levels.
- Investing in biomass projects: Consider investing in biomass energy projects or supporting crowdfunding initiatives that aim to promote sustainable energy solutions.
- Exploring personal biomass options: Individuals can explore the use of biomass energy in their own homes, such as through the installation of pellet stoves or boilers.
An expert would offer specific recommendations for individuals to contribute to the growth of biomass energy, emphasizing the importance of collective action and raising awareness.
- Recommended organizations or initiatives supporting biomass energy
- Case studies on successful implementation of biomass energy at the individual level