how to get biomass energy
September 01, 2024
Published
October 25, 2023
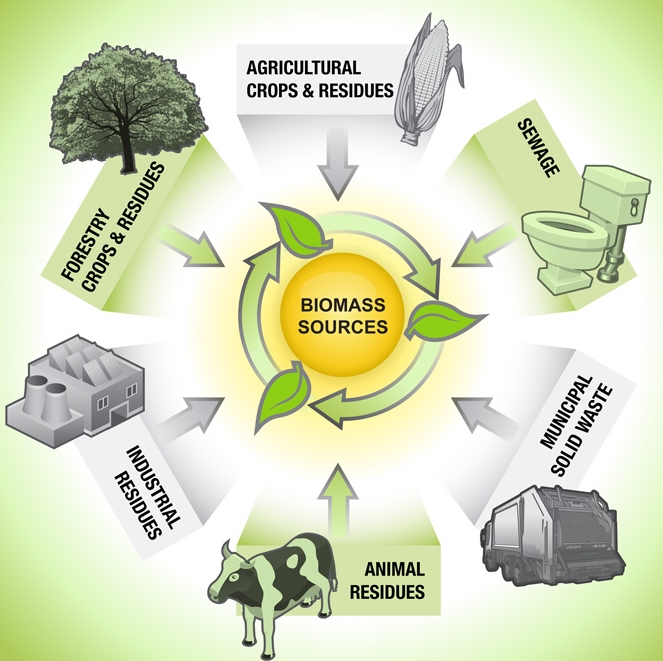
Types of Biomass
Trang thông tin điện tử về Năng lượng sinh khối
Frequently Asked Questions about Biomass
1. What is biomass? Biomass is organic material derived from plants and animals. It can include agricultural crops, forestry materials, and even municipal and industrial waste. 2. What are the benefits of using biomass as an energy source?
Biomass is organic material derived from plants and animals. It can include agricultural crops, forestry materials, and even municipal and industrial waste. 2. What are the benefits of using biomass as an energy source?  - Biomass is a renewable energy source, meaning it can be replenished over time. - It can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions as it releases fewer pollutants compared to fossil fuels. - Biomass can be used for heat, electricity, and transportation fuel, providing a versatile energy solution. - It contributes to waste management by utilizing organic materials that would otherwise be disposed of in landfills. 3. How is biomass converted into energy?
- Biomass is a renewable energy source, meaning it can be replenished over time. - It can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions as it releases fewer pollutants compared to fossil fuels. - Biomass can be used for heat, electricity, and transportation fuel, providing a versatile energy solution. - It contributes to waste management by utilizing organic materials that would otherwise be disposed of in landfills. 3. How is biomass converted into energy?  There are several processes to convert biomass into energy: - Direct combustion: Biomass is burned to produce heat, which can be used for various applications. - Anaerobic digestion: Biomass is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used as fuel. - Gasification: Biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment to produce syngas, which can be further processed into biofuels or used for heating and electricity generation. - Pyrolysis: Biomass is heated in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of biochar, bio-oil, and gases that can be used for energy. 4. Is biomass energy sustainable?
There are several processes to convert biomass into energy: - Direct combustion: Biomass is burned to produce heat, which can be used for various applications. - Anaerobic digestion: Biomass is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used as fuel. - Gasification: Biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment to produce syngas, which can be further processed into biofuels or used for heating and electricity generation. - Pyrolysis: Biomass is heated in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of biochar, bio-oil, and gases that can be used for energy. 4. Is biomass energy sustainable?  Biomass energy can be sustainable if managed properly. It relies on using organic waste and residues that would otherwise end up in landfills, reducing waste and utilizing available resources. However, unsustainable practices such as deforestation for biomass production can have negative environmental impacts. It is essential to ensure that biomass is sourced from sustainable sources and managed responsibly to maintain its sustainability. 5. Can biomass energy replace fossil fuels?
Biomass energy can be sustainable if managed properly. It relies on using organic waste and residues that would otherwise end up in landfills, reducing waste and utilizing available resources. However, unsustainable practices such as deforestation for biomass production can have negative environmental impacts. It is essential to ensure that biomass is sourced from sustainable sources and managed responsibly to maintain its sustainability. 5. Can biomass energy replace fossil fuels?  While biomass energy has the potential to replace some portion of fossil fuels, it is unlikely to completely replace them. Biomass has its limitations in terms of scalability and energy density. It can play a significant role in a diversified and sustainable energy portfolio by providing renewable energy and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. 6. Are there any challenges associated with biomass energy?
While biomass energy has the potential to replace some portion of fossil fuels, it is unlikely to completely replace them. Biomass has its limitations in terms of scalability and energy density. It can play a significant role in a diversified and sustainable energy portfolio by providing renewable energy and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. 6. Are there any challenges associated with biomass energy?  Some challenges associated with biomass energy include: - Availability and access to biomass feedstock: Sourcing sufficient biomass can be a challenge, especially in areas with limited agricultural or forestry resources. - Cost-effectiveness: The cost of biomass energy production and conversion technologies can be higher compared to conventional fossil fuel options. - Environmental impacts: Improper management of biomass production and conversion can result in negative environmental impacts, such as deforestation and increased air pollution. - Public acceptance: Biomass energy facilities may face resistance from nearby communities due to concerns about noise, odor, and other perceived negative impacts. 7. Can biomass energy contribute to rural development?
Some challenges associated with biomass energy include: - Availability and access to biomass feedstock: Sourcing sufficient biomass can be a challenge, especially in areas with limited agricultural or forestry resources. - Cost-effectiveness: The cost of biomass energy production and conversion technologies can be higher compared to conventional fossil fuel options. - Environmental impacts: Improper management of biomass production and conversion can result in negative environmental impacts, such as deforestation and increased air pollution. - Public acceptance: Biomass energy facilities may face resistance from nearby communities due to concerns about noise, odor, and other perceived negative impacts. 7. Can biomass energy contribute to rural development?  Yes, biomass energy can contribute to rural development in several ways: - Job creation: Biomass production, collection, and processing can provide employment opportunities in rural areas. - Local economic development: Biomass energy projects can stimulate local economies through investments, revenue generation, and increased demand for related goods and services. - Energy independence: Biomass energy can reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, providing energy security for rural communities. - Utilization of local resources: Biomass energy utilizes locally available organic materials, making use of resources that may otherwise go to waste. 8. What are the current trends in biomass energy utilization?
Yes, biomass energy can contribute to rural development in several ways: - Job creation: Biomass production, collection, and processing can provide employment opportunities in rural areas. - Local economic development: Biomass energy projects can stimulate local economies through investments, revenue generation, and increased demand for related goods and services. - Energy independence: Biomass energy can reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, providing energy security for rural communities. - Utilization of local resources: Biomass energy utilizes locally available organic materials, making use of resources that may otherwise go to waste. 8. What are the current trends in biomass energy utilization?  Some current trends in biomass energy utilization include: - Use of advanced conversion technologies: Research and development are ongoing to develop more efficient and cost-effective biomass conversion technologies, such as biofuel production from lignocellulosic feedstocks. - Integration with other renewable energy sources: Biomass energy can be integrated with other renewable energy sources like solar and wind to provide a more reliable and consistent energy supply. - Decentralized energy systems: Biomass energy can be used in decentralized systems, allowing for local energy production and utilization. - Bioenergy villages and communities: Communities are exploring the concept of becoming self-sufficient in their energy needs through the use of local biomass resources. 9. How does biomass energy impact the environment?
Some current trends in biomass energy utilization include: - Use of advanced conversion technologies: Research and development are ongoing to develop more efficient and cost-effective biomass conversion technologies, such as biofuel production from lignocellulosic feedstocks. - Integration with other renewable energy sources: Biomass energy can be integrated with other renewable energy sources like solar and wind to provide a more reliable and consistent energy supply. - Decentralized energy systems: Biomass energy can be used in decentralized systems, allowing for local energy production and utilization. - Bioenergy villages and communities: Communities are exploring the concept of becoming self-sufficient in their energy needs through the use of local biomass resources. 9. How does biomass energy impact the environment?  The environmental impacts of biomass energy can vary depending on various factors, including feedstock sourcing, conversion processes, and regulatory standards. Some potential environmental impacts include: - Air pollution: Biomass combustion can emit pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. However, advanced emission control technologies can minimize these impacts. - Water usage: Biomass energy production may require significant amounts of water, especially in certain conversion processes. Water management practices should be implemented to minimize water consumption and protect water resources. - Land use and biodiversity: Biomass cultivation or harvesting for energy purposes can impact land use and biodiversity. Sustainable land management practices and proper land-use planning are essential to minimize these impacts. 10. Can biomass energy be used in vehicles?
The environmental impacts of biomass energy can vary depending on various factors, including feedstock sourcing, conversion processes, and regulatory standards. Some potential environmental impacts include: - Air pollution: Biomass combustion can emit pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. However, advanced emission control technologies can minimize these impacts. - Water usage: Biomass energy production may require significant amounts of water, especially in certain conversion processes. Water management practices should be implemented to minimize water consumption and protect water resources. - Land use and biodiversity: Biomass cultivation or harvesting for energy purposes can impact land use and biodiversity. Sustainable land management practices and proper land-use planning are essential to minimize these impacts. 10. Can biomass energy be used in vehicles?  Yes, biomass energy can be used in vehicles through the production of biofuels. Biomass-based biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, can be blended with or used as a substitute for gasoline and diesel fuels. However, the availability and infrastructure for biofuel production and distribution may vary across different regions. 11. Is biomass energy economically viable?
Yes, biomass energy can be used in vehicles through the production of biofuels. Biomass-based biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, can be blended with or used as a substitute for gasoline and diesel fuels. However, the availability and infrastructure for biofuel production and distribution may vary across different regions. 11. Is biomass energy economically viable?  The economic viability of biomass energy depends on various factors, including the availability and cost of biomass feedstock, conversion technologies, and government policies and incentives. In some cases, biomass energy may be economically competitive with fossil fuels, while in others, it may require financial support or favorable market conditions to be economically viable. 12. What is the future outlook for biomass energy?
The economic viability of biomass energy depends on various factors, including the availability and cost of biomass feedstock, conversion technologies, and government policies and incentives. In some cases, biomass energy may be economically competitive with fossil fuels, while in others, it may require financial support or favorable market conditions to be economically viable. 12. What is the future outlook for biomass energy?  The future outlook for biomass energy is promising, with ongoing advancements in conversion technologies, sustainability practices, and policy support. Biomass energy can play a crucial role in transitioning to a more sustainable and low-carbon energy system. Continued research, innovation, and investment in biomass energy can further enhance its potential and contribution to global energy goals.
The future outlook for biomass energy is promising, with ongoing advancements in conversion technologies, sustainability practices, and policy support. Biomass energy can play a crucial role in transitioning to a more sustainable and low-carbon energy system. Continued research, innovation, and investment in biomass energy can further enhance its potential and contribution to global energy goals.